Metabarcoding workflow for 12S amplicon sequencing with Riaz primers
page details in progress.
The 12S rRNA gene region of the mitogenome is ~950 bp. There are two popular primer sets to amplify two different regions of 12S: Riaz and MiFish. The following workflow includes script specific to the Riaz primer set, but includes some notes on the MiFish U/E primer set.
If working on the NU system, 'Discovery' cluster is the old system that used the path (/work) and 'Explorer' is the new system that uses the path (/projects).
Riaz ecoPrimers citation: Riaz et al. 2011
MiFish citation: Miya et al. 2015
Analysis workflow:
1. Assess quality of fastq files using FASTQC and MultiQC
2. Identify sequencing outliers and sub-sample if needed
3. Run nf-core/ampliseq to remove adapters, predict ASVs, and generate counts tables
4. Run blastn to assign taxonomy from three databases: GMGI's, Mitofish, and NCBI
Prerequisite: Confirm conda environment is available and activate
The conda environment is started within each slurm script, but to activate conda environment outside of the slurm script to update packages or check what is installed:
# Activate fisheries eDNA conda environment
source /projects/gmgi/miniconda3/bin/activate fisheries_eDNA
# List all available environments
conda env list
# List all packages installed in fisheries_eDNA
conda list
# Update a package
conda update [package name]
# Update nextflow ampliseq workflow
nextflow pull nf-core/ampliseq
Step 1: Assess quality of fastq files using FASTQC and MultiQC
Assessing quality with FASTQC
Background information on FASTQC. For eDNA files, this program is extremely quick. Expect <10 seconds per sample when running in an array.
01-fastqc.sh:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --error=output/fastqc_output/"%x_error.%j" #if your job fails, the error report will be put in this file
#SBATCH --output=output/fastqc_output/"%x_output.%j" #once your job is completed, any final job report comments will be put in this file
#SBATCH --partition=short
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --time=4:00:00
#SBATCH --job-name=01-fastqc
#SBATCH --mem=1GB
#SBATCH --ntasks=1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=1
### USER TO-DO ###
## 1. Set paths for your project
# Activate conda environment
source /projects/gmgi/miniconda3/bin/activate fisheries_eDNA
## SET PATHS (CHANGE THESE TO PROJECT SPECIFIC)
raw_path=""
out_dir=""
## CREATE SAMPLE LIST FOR SLURM ARRAY
### 1. Create list of all .gz files in raw data path
ls -d ${raw_path}/*.gz > ${raw_path}/rawdata
### 2. Create a list of filenames based on that list created in step 1
mapfile -t FILENAMES < ${raw_path}/rawdata
### 3. Create variable i that will assign each row of FILENAMES to a task ID
i=${FILENAMES[$SLURM_ARRAY_TASK_ID]}
## RUN FASTQC PROGRAM
fastqc ${i} --outdir ${out_dir}
To run:
- Start slurm array with file 0 (e.g., with 138 files) = sbatch --array=0-137 00-fastqc.sh.
Path examples:
- raw_path="/projects/gmgi/Fisheries/eDNA/tidal_cycle/raw_data"
- out_dir="/projects/gmgi/Fisheries/eDNA/tidal_cycle/fastqc_output"
Notes:
- This is going to output many error and output files. After job completes, use
cat *output.* > ../fastqc_output.txtto create one file with all the output andcat *error.* > ../fastqc_error.txtto create one file with all of the error message outputs. - Within the
out_diroutput folder, usels *html | wcto count the number of html output files (1st/2nd column values). This should be equal to the --array range used and the number of raw data files. If not, the script missed some input files so address this before moving on.
Visualize quality with MULTIQC
Background information on MULTIQC.
Run the following code in an interactive node. This program will be quick for eDNA data (typically <2 minutes).
# Use srun to claim a node
srun --pty bash
# Activate conda environment
source /projects/gmgi/miniconda3/bin/activate fisheries_eDNA
## SET PATHS
## fastqc_output = output from 00-fastqc.sh; fastqc program
fastqc_output=""
multiqc_dir=""
## RUN MULTIQC
### Navigate to your project
multiqc --interactive ${fastqc_output} -o ${multiqc_dir} --filename multiqc_raw.html
Path examples:
- fastqc_output="/projects/gmgi/Fisheries/eDNA/tidal_cycle/fastqc_output"
- multiqc_dir="/projects/gmgi/Fisheries/eDNA/tidal_cycle"
Step 2: Identify sequencing outliers and sub-sample if needed
This step can be done two ways: 1) download read counts from Illumina basespace run information or 2) Download read counts from the multiqc report. Either way, you need an excel file with the sample ID and total read count.
Read counts can be downloaded from the General Statistics section on Multiqc by selecting Export as CSV > Data > Format (csv) > Download Plot Data. Save this file in the project repository.

We use a median absolute deviation (MAD) approach that works by first finding the median of the data, then measuring how far each value deviates from that median and using the median of those deviations as the typical spread. Values whose deviation is much larger than this typical spread are flagged as outliers.
Visit this page for the R script or download here.
Download seqtk program
This program has already been installed on NU with the below code:
# move to gmgi/packages folder
cd /projects/gmgi/packages/
# download seqtk program from their github page; move into that folder; and enable (`make`) the program
# ; indicates a pipe much like %>% in R
git clone https://github.com/lh3/seqtk.git;
cd seqtk; make
Path to the program: /projects/gmgi/packages/seqtk/seqtk
Running seqtk with a single (or handful) of samples
Calculate the median number of reads prior to this code. This example will use 70,377.
# start an interactive session on 1 node
srun --pty bash
# cd to your raw data folder
# make a new folder called outliers (`mkdir` = make directory)
mkdir outliers
# define a path to reference later using ${seqtk}
seqtk="/projects/gmgi/packages/seqtk/seqtk"
# reference the program path above using ${} and subsample the original fastq file
# to 70,377 reads using a set seed of -s100 following by gzipping that file using a pipe |
# that is similar to %>% in R. I have two commands then: 1) sub-sample 2) gzip
# > indicates a new output file
${seqtk} sample -s100 INS2-FS-0011_S284_L001_R1_001.fastq.gz 70377 | gzip > INS2-FS-0011_S284_L001_R1_001_subset.fastq.gz
${seqtk} sample -s100 INS2-FS-0011_S284_L001_R2_001.fastq.gz 70377 | gzip > INS2-FS-0011_S284_L001_R2_001_subset.fastq.gz
# move original files into the outliers folders so they are out of the way of our analysis
mv INS2-FS-0011_S284_L001_R1_001.fastq.gz outliers/
mv INS2-FS-0011_S284_L001_R2_001.fastq.gz outliers/
Running seqtk with a list of files
Create a samplesheet using 03a-metadata.R below as an example. If you have a csv with 'sampleID', 'forwardReads', and 'reverseReads' columns then turn that csv into a text file with:
tail -n +2 outlier_list_for_subsampling.csv | cut -d',' -f2,3 | tr ',' '\n' > outlier_paths.txt
The input to the below .sh is a txt file with a single column with no header that lists the full path of each fastq file to subset.
02-outlier.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --error=output/"%x_error.%j" #if your job fails, the error report will be put in this file
#SBATCH --output=output/"%x_output.%j" #once your job is completed, any final job report comments will be put in this file
#SBATCH --partition=short
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --time=4:00:00
#SBATCH --job-name=02-outlier
#SBATCH --mem=1GB
#SBATCH --ntasks=1
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=1
### Running seqtk for a list of files
# path to seqtk
seqtk="/projects/gmgi/packages/seqtk/seqtk"
# input list
input_list="/projects/gmgi/oceanX/2025_CVDD_puffer-transect/18S_v8v9/outlier_paths.txt"
# directory for subset files
output_directory="/projects/gmgi/oceanX/2025_CVDD_puffer-transect/18S_v8v9/combined_rawdata"
# directory to archive files
archive_directory="/projects/gmgi/oceanX/2025_CVDD_puffer-transect/18S_v8v9/combined_rawdata/outliers"
# number of reads
nreads=70377
seed=100
# Run seqtk on the input_list files
while read -r fq; do
[[ -z "$fq" ]] && continue
base=$(basename "$fq" .fastq.gz)
out="${output_directory}/${base}_subset.fastq.gz"
echo "Subsampling: $fq -> $out"
"${seqtk}" sample -s"${seed}" "$fq" "${nreads}" | gzip > "$out"
done < "$input_list"
# Move input_list files to the archive folder
mkdir -p "$archive_directory"
while read -r fq; do
[[ -z "$fq" ]] && continue
echo "Archiving: $fq -> $archive_directory"
mv "$fq" "$archive_directory/"
done < "$input_list"
Step 3: Run nf-core/ampliseq to remove adapters, predict ASVs, and generate counts tables
Nf-core and ampliseq pipeline description
Nf-core: A community effort to collect a curated set of analysis pipelines built using Nextflow.
Nextflow: scalable and reproducible scientific workflows using software containers, used to build wrapper programs like the one we use here.
[https://nf-co.re/ampliseq/2.11.0]: nfcore/ampliseq is a bioinformatics analysis pipeline used for amplicon sequencing, supporting denoising of any amplicon and supports a variety of taxonomic databases for taxonomic assignment including 16S, ITS, CO1 and 18S.
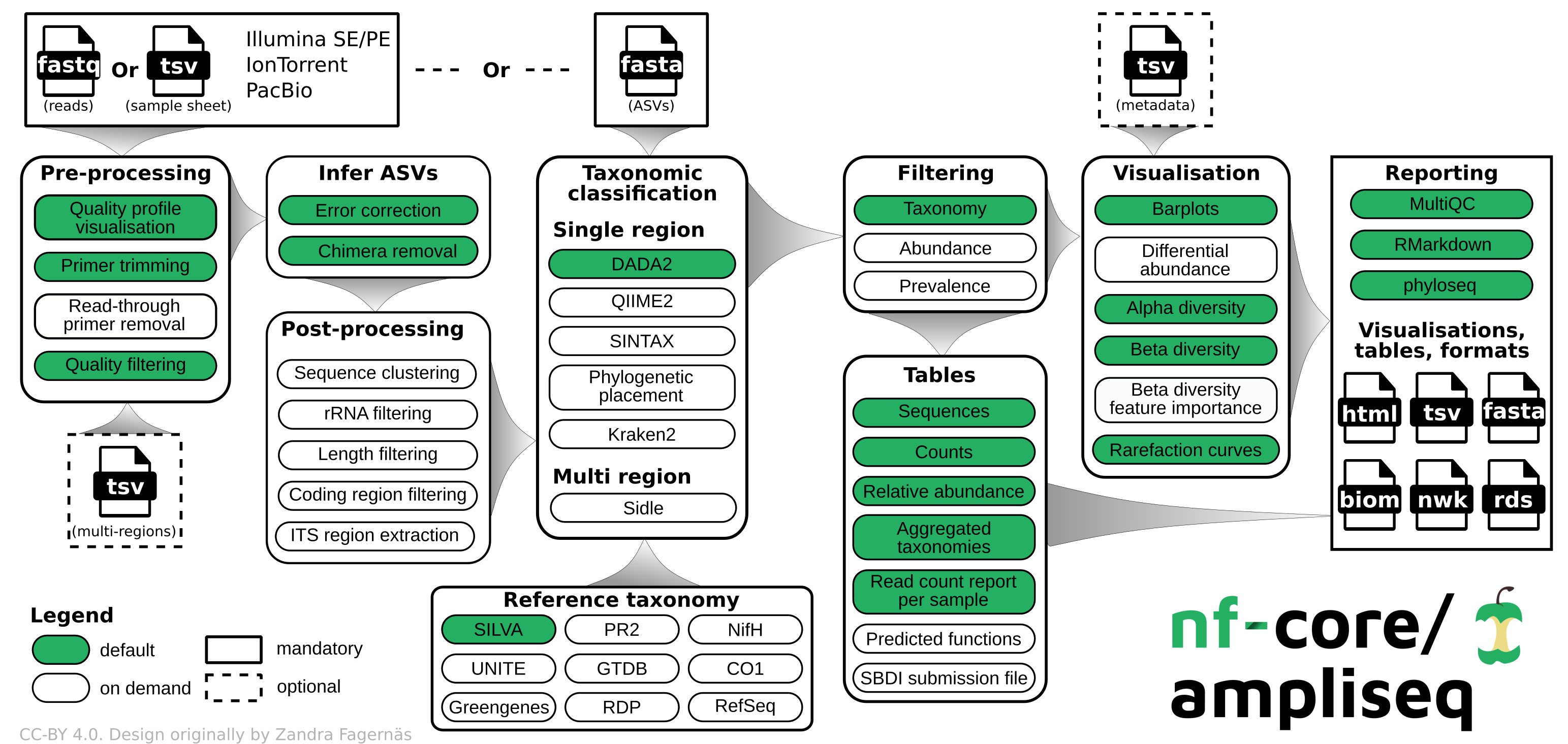
We use ampliseq for the following programs:
- Cutadapt is trimming primer sequences from sequencing reads. Primer sequences are non-biological sequences that often introduce point mutations that do not reflect sample sequences. This is especially true for degenerated PCR primer. If primer trimming would be omitted, artifactual amplicon sequence variants might be computed by the denoising tool or sequences might be lost due to become labelled as PCR chimera.
- DADA2 performs fast and accurate sample inference from amplicon data with single-nucleotide resolution. It infers exact amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) from amplicon data with fewer false positives than many other methods while maintaining high sensitivity.
We skip the taxonomic assignment because we use 3-db approach described in the next section.
12S primer sequences (required)
Below is what we used for 12S amplicon sequencing. Ampliseq will automatically calculate the reverse compliment and include this for us.
Riaz 12S amplicon F Original: ACTGGGATTAGATACCCC
Riaz 12S amplicon F Degenerate: ACTGGGATTAGATACCCY
Riaz 12S amplicon R: TAGAACAGGCTCCTCTAG
MiFish primer set:
MiFish-U 12S amplicon F: GTCGGTAAAACTCGTGCCAGC
MiFish-U 12S amplicon R: CATAGTGGGGTATCTAATCCCAGTTTG
MiFish-E 12S amplicon F: GTTGGTAAATCTCGTGCCAGC
MiFish-E 12S amplicon R: CATAGTGGGGTATCTAATCCTAGTTTG
Metadata sheet (optional)
The metadata file has to follow the QIIME2 specifications. Below is a preview of the sample sheet used for this test. Keep the column headers the same for future use. The first column needs to be "ID" and can only contain numbers, letters, or "-". This is different than the sample sheet. NAs should be empty cells rather than "NA".
Create samplesheet sheet for ampliseq
This file indicates the sample ID and the path to R1 and R2 files. Below is a preview of the sample sheet used in this test. File created on RStudio Interactive on Discovery Cluster using (create_metadatasheets.R).
- sampleID (required): Unique sample IDs, must start with a letter, and can only contain letters, numbers or underscores (no hyphons!).
- forwardReads (required): Paths to (forward) reads zipped FastQ files
- reverseReads (optional): Paths to reverse reads zipped FastQ files, required if the data is paired-end
- run (optional): If the data was produced by multiple sequencing runs, any string
| sampleID | forwardReads | reverseReads | run |
|---|---|---|---|
| sample1 | ./data/S1_R1_001.fastq.gz | ./data/S1_R2_001.fastq.gz | A |
| sample2 | ./data/S2_fw.fastq.gz | ./data/S2_rv.fastq.gz | A |
| sample3 | ./S4x.fastq.gz | ./S4y.fastq.gz | B |
| sample4 | ./a.fastq.gz | ./b.fastq.gz | B |
This is an R script, not slurm script. Open RStudio interactive on Discovery Cluster to run this script.
Prior to running R script, use the rawdata file created for the fastqc slurm array from within the raw data folder to create a list of files. Below is an example from our Offshore Wind project but the specifics of the sampleID will be project dependent. This project had four sequencing runs with different file names.
03a-metadata.R
## Load libraries
library(dplyr)
library(stringr)
library(strex)
### Read in sample sheet
### CHANGE THE PATH HERE
sample_list <- read.delim2("/rawdata", header=F) %>%
dplyr::rename(forwardReads = V1) %>%
mutate(sampleID = str_after_nth(forwardReads, "data/", 1),
sampleID = str_before_nth(sampleID, "_S", 1))
# creating sample ID
sample_list$sampleID <- gsub("-", "_", sample_list$sampleID)
# keeping only rows with R1
sample_list <- filter(sample_list, grepl("R1", forwardReads, ignore.case = TRUE))
# duplicating column
sample_list$reverseReads <- sample_list$forwardReads
# replacing R1 with R2 in only one column
sample_list$reverseReads <- gsub("R1", "R2", sample_list$reverseReads)
# rearranging columns
sample_list <- sample_list[,c(2,1,3)]
### CHANGE THE PATH HERE
sample_list %>% write.csv("/samplesheet.csv",
row.names=FALSE, quote = FALSE)
Path example:
- ""
Run nf-core/ampliseq (Cutadapt & DADA2)
Update ampliseq workflow if needed: nextflow pull nf-core/ampliseq.
Important to confirm that the samplesheet.csv you're using includes the subsetted fastq files (if any).
Below script is set for Riaz primers:
03b-ampliseq.sh:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --error=output/"%x_error.%j" #if your job fails, the error report will be put in this file
#SBATCH --output=output/"%x_output.%j" #once your job is completed, any final job report comments will be put in this file
#SBATCH --partition=short
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --time=20:00:00
#SBATCH --job-name=ampliseq
#SBATCH --mem=70GB
#SBATCH --ntasks=24
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=2
### USER TO-DO ###
## 1. Set paths for project
## 2. Adjust SBATCH options above (time, mem, ntasks, etc.) as desired
## 3. Fill in F primer information based on primer type (no reverse compliment needed)
## 4. Adjust parameters as needed (below is Fisheries team default for 12S)
# Load nextflow conda environment
source /projects/gmgi/miniconda3/bin/activate nextflow_env
# SET PATHS
metadata=""
output_dir=""
nextflow run nf-core/ampliseq -resume \
-profile singularity \
--input ${metadata}/samplesheet.csv \
--FW_primer "" \
--RV_primer "TAGAACAGGCTCCTCTAG" \
--outdir ${output_dir} \
--trunclenf 100 \
--trunclenr 100 \
--trunc_qmin 25 \
--max_len 200 \
--max_ee 2 \
--min_len_asv 80 \
--max_len_asv 115 \
--sample_inference pseudo \
--skip_taxonomy \
--ignore_failed_trimming
To run:
- sbatch 03b-ampliseq.sh
Discovery needs module load singularity/3.10.3 and module load nextflow/24.04.4, but on Explorer this is just module load nextflow/24.10.3.
MiFish amplifies a longer target region which requires 2x250 bp sequencing (500 cycle kit). Thus following edits are required if using MiFish primers:
- F/R primer correct sequences
- Edit --min_len_asv, --max_len_asv to reflect the correct target region length
- Edit --trunclenf, --trunclenr, --max_len to reflect correct trimming length for longer reads
Files generated by ampliseq
Pipeline summary reports:
summary_report/summary_report.html: pipeline summary report as standalone HTML file that can be viewed in your web browser.*.svg*: plots that were produced for (and are included in) the report.versions.yml: software versions used to produce this report.
Preprocessing:
- FastQC:
fastqc/and*_fastqc.html: FastQC report containing quality metrics for your untrimmed raw fastq files. - Cutadapt:
cutadapt/andcutadapt_summary.tsv: summary of read numbers that pass cutadapt - MultiQC:
multiqc,multiqc_data/,multiqc_plots/withmultiqc_report.html: a standalone HTML file that can be viewed in your web browser;
ASV inferrence with DADA2:
dada2/,dada2/args/,data2/log/ASV_seqs.fasta: Fasta file with ASV sequences.ASV_table.tsv: Counts for each ASV sequence.DADA2_stats.tsv: Tracking read numbers through DADA2 processing steps, for each sample.DADA2_table.rds: DADA2 ASV table as R object.DADA2_table.tsv: DADA2 ASV table.dada2/QC/*.err.convergence.txt: Convergence values for DADA2's dada command, should reduce over several magnitudes and approaching 0.*.err.pdf: Estimated error rates for each possible transition. The black line shows the estimated error rates after convergence of the machine-learning algorithm. The red line shows the error rates expected under the nominal definition of the Q-score. The estimated error rates (black line) should be a good fit to the observed rates (points), and the error rates should drop with increased quality.*_qual_stats.pdf: Overall read quality profiles: heat map of the frequency of each quality score at each base position. The mean quality score at each position is shown by the green line, and the quartiles of the quality score distribution by the orange lines. The red line shows the scaled proportion of reads that extend to at least that position.*_preprocessed_qual_stats.pdf: Same as above, but after preprocessing.
We add an ASV length filter that will output asv_length_filter/ with:
ASV_seqs.len.fasta: Fasta file with filtered ASV sequences.ASV_table.len.tsv: Counts for each filtered ASV sequence.ASV_len_orig.tsv: ASV length distribution before filtering.ASV_len_filt.tsv: ASV length distribution after filtering.stats.len.tsv: Tracking read numbers through filtering, for each sample.
Step 5: Blast ASV sequences (output from DADA2) against our 3 databases
Note that the GMGI-12S database will not apply to the MiFish primer sets so only Mitofish and NCBI are required.
Populating /projects/gmgi/databases folder
We use NCBI, Mitofish, and GMGI-12S databases.
Download and/or update NBCI blast nt database
NCBI is updated daily and therefore needs to be updated each time a project is analyzed. This is the not the most ideal method but we were struggling to get the -remote flag to work within slurm because I don't think NU slurm is connected to the internet? NU help desk was helping for awhile but we didn't get anywhere.
Within /projects/gmgi/databases/ncbi, there is a update_nt.sh script with the following code. To run sbatch update_nt.sh. This won't take long as it will check for updates rather than re-downloading every time.
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --partition=short
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --time=24:00:00
#SBATCH --job-name=update_ncbi_nt
#SBATCH --mem=50G
#SBATCH --output=%x_%j.out
#SBATCH --error=%x_%j.err
# Activate conda environment
source /projects/gmgi/miniconda3/bin/activate fisheries_eDNA
# Create output directory if it doesn't exist
cd /projects/gmgi/databases/ncbi/nt
# Update BLAST nt database
update_blastdb.pl --decompress nt
# Print completion message
echo "BLAST nt database update completed"
View the update_ncbi_nt.out file to confirm the echo printed at the end.
Download and/or update Mitofish database
Check Mitofish webpage for the most recent database version number. Compare to the projects/gmgi/databases/12S folder. If needed, update Mitofish database with the below code.
- Move the old database to the
archve/folder within/projects/gmgi/databases/12S/Mitofish. - Use
wgetwith the link to the new db (egwget https://mitofish.aori.u-tokyo.ac.jp/download/fullseq/2025/06/mitofishdb.fa.gz). - Use
wgetto download tables file (egwget https://mitofish.aori.u-tokyo.ac.jp/download/tables/2025/06/tables.tar) - Run
update_mitofish.shby usingsbatch update_mitofish.sh v2025.06. Replace the version # as needed.
update_mitofish.sh
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --error=update_mito_err/"%x_error.%j" #if your job fails, the error report will be put in this file
#SBATCH --output=update_mito_err/"%x_output.%j" #once your job is completed, any final job report comments will be put in this file
#SBATCH --partition=short
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --time=1:00:00
#SBATCH --job-name=update_mitofish
#SBATCH --mem=5GB
#SBATCH --ntasks=2
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=2
## Activate conda environment
source /projects/gmgi/miniconda3/bin/activate fisheries_eDNA
## make NCBI db
gunzip mitofishdb.fa.gz
makeblastdb -in mitofishdb.fa -dbtype nucl -out mitofishdb -parse_seqids
## create csv files from parquet files
tar -xvf tables.tar
for f in *.parquet; do
parquet-tools csv "$f" > "${f%.parquet}.csv"
done
## merge parquet-derived CSVs to provide one db csv
python - <<'PY'
import pandas as pd
df = (
pd.read_csv("seq_taxonid.csv")
.merge(pd.read_csv("taxonid_speciesid.csv"), on="taxon_id", how="left")
.merge(pd.read_csv("speciesid_lineageid.csv"), on="species_id", how="left")
.merge(pd.read_csv("taxonid_name.csv"), on="lineage_id", how="left")
)
df.to_csv("mitofish_merged_taxonomy.csv", index=False)
PY
# --- add version prefix to files in this directory ---
# Excludes directories, the script itself, and anything already prefixed.
version="$1"
script_name="$(basename "$0")"
for f in *; do
[[ -f "$f" ]] || continue
[[ "$f" == *.sh ]] && continue
[[ "$f" == "${version}_"* ]] && continue
mv -- "$f" "${version}_$f"
done
Download GMGI 12S
This is our in-house GMGI database that will include version numbers. Check /projects/gmgi/databases/12S/GMGI/ for current uploaded version number and check our Box folder for the most recent version number.
On OOD portal, click the Interactive Apps dropdown. Select Home Directory under the HTML Viewer section. Navigate to the /projects/gmgi/databases/12S/GMGI/ folder. In the top right hand corner of the portal, select Upload and add the most recent .fasta file from our Box folder.
To create a blast db from this reference fasta file (if updated):
cd /projects/gmgi/databases/12S/GMGI/
## make NCBI db
## make sure fisheries_eDNA conda environment is activated
### CHANGE THE VERSION NUMBER BELOW TO LATEST
makeblastdb -in GMGI_Vert_Ref_2024v1.fasta -dbtype nucl -out GMGI_Vert_Ref_2024v1.fasta
Running taxonomic ID script
Download taxonkit to your home directory. You only need to do this once, otherwise the program is set-up and you can skip this step. Taxonkit program is in /projects/gmgi/databases/taxonkit but the program needs required files to be in your home directory.
# Move to home directory and download taxonomy information
cd ~
wget -c ftp://ftp.ncbi.nih.gov/pub/taxonomy/taxdump.tar.gz
# Extract the downloaded file
tar -zxvf taxdump.tar.gz
# Create the TaxonKit data directory
mkdir -p $HOME/.taxonkit
# Copy the required files to the TaxonKit data directory
cp names.dmp nodes.dmp delnodes.dmp merged.dmp $HOME/.taxonkit
04-taxonomicID.sh:
#!/bin/bash
#SBATCH --error=output/"%x_error.%j" #if your job fails, the error report will be put in this file
#SBATCH --output=output/"%x_output.%j" #once your job is completed, any final job report comments will be put in this file
#SBATCH --partition=short
#SBATCH --nodes=1
#SBATCH --time=20:00:00
#SBATCH --job-name=tax_ID
#SBATCH --mem=30GB
#SBATCH --ntasks=24
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=2
### USER TO-DO ###
## 1. Set paths for project; change db path if not 12S
# Activate conda environment
source /projects/gmgi/miniconda3/bin/activate fisheries_eDNA
# SET PATHS
ASV_fasta=""
out=""
gmgi="/projects/gmgi/databases/12S/GMGI"
mito="/projects/gmgi/databases/12S/Mitofish"
ncbi="/projects/gmgi/databases/ncbi/nt"
taxonkit="/projects/gmgi/databases/taxonkit"
#### DATABASE QUERY ####
### NCBI database
blastn -db ${ncbi}/"nt" \
-query ${ASV_fasta}/ASV_seqs.len.fasta \
-out ${out}/BLASTResults_NCBI.txt \
-max_target_seqs 10 -perc_identity 100 -qcov_hsp_perc 95 \
-outfmt '6 qseqid sseqid sscinames staxid pident length mismatch gapopen qstart qend sstart send evalue bitscore'
## Mitofish database
blastn -db ${mito}/*.fasta \
-query ${ASV_fasta}/ASV_seqs.len.fasta \
-out ${out}/BLASTResults_Mito.txt \
-max_target_seqs 10 -perc_identity 100 -qcov_hsp_perc 95 \
-outfmt '6 qseqid sseqid pident length mismatch gapopen qstart qend sstart send evalue bitscore'
## GMGI database
blastn -db ${gmgi}/*.fasta \
-query ${ASV_fasta}/ASV_seqs.len.fasta \
-out ${out}/BLASTResults_GMGI.txt \
-max_target_seqs 10 -perc_identity 98 -qcov_hsp_perc 95 \
-outfmt '6 qseqid sseqid pident length mismatch gapopen qstart qend sstart send evalue bitscore'
############################
#### TAXONOMIC CLASSIFICATION ####
## creating list of staxids from all three files
awk -F $'\t' '{ print $4}' ${out}/BLASTResults_NCBI.txt | sort -u > ${out}/NCBI_sp.txt
## annotating taxid with full taxonomic classification
cat ${out}/NCBI_sp.txt | ${taxonkit}/taxonkit reformat -I 1 -r "Unassigned" > ${out}/NCBI_taxassigned.txt
To run:
- sbatch 04-taxonomicID.sh